AyMINE – Technical documentation
Modules
 Task, project & quality management
Task, project & quality management
Manager approval with the task report
Why some data can't be deleted
Adminitration of areas, projects, calendars
Region / project / methodology
Change management process in a project
GDPR and record of qualifications
Qualification of user or contact
Right to Manage Qualifications
Failure Analysis for an Individual Property of a Component or Process
FMEA – Probability of Detection
FMEA – Probability of Occurrence
 Task, project & quality management
Task, project & quality management
Administration of the Task Management Module
System rights for the task management module
Improvements and Preventive Measures
Methodology and Quality Management systems
What a methodology / QMS consists of
Problems, tickets and their management
Collaborative Resolution of Multiple Problems
Customer Service Response Generation
Incident and Quality Issue Management
Objects affected by the problem
Problems, Incidents, Helpdesk Tickets
Return project plan by baseline
Sample tasks and methodologies of the area
Effect of the task on the right to modify the attached object
The person responsible for the task
Working procedure – task definition
Objects related to the task pattern
 Contacts and directories module (CRM)
Contacts and directories module (CRM)
Order overview for customer groups
 Contacts and directories module (CRM)
Contacts and directories module (CRM)
System Permissions and CRM Module Settings
Send bulk messages in compliance with GDPR
How to correctly forget a person's details
Unsubscribe and set preferences
for bulk mail
 Web management and automation
Web management and automation
Receiving a message from the web
Human resources
Personalistics – User Permissions
Human Resources module security
Manage department / division data
Overview of Personnel Information for pracov# Employment Contract
Synchronizing staff and system users
 Products, assets and sales
Products, assets and sales
Received order for goods or services
Finance management
Metrics and Measurements
Technical Modules
Sabre plugin module
Enterprise Architect connector
Database link to Enterprise Architect database
Enterprise Architect connector
System Modules
 The AyMINE Framework Module
The AyMINE Framework Module
AyMINE — Tips for Mobile Usage
Configure how your system looks and works
Gestures and Keyboard Shortcuts
More about how the system works
Private notes and tags for objects
Overview of Modules and Record Types
Filtering in the list of records
 System Management
System Management
Additional functions with files
Copying and moving files between objects
Files (documents) linked to the object
Formatted texts in the application
Gateway settings for external messages
IMP gateway settings for email communication
Internet Call Gateway Settings
Message with the outside world
 FMEA – Probability of Detection
FMEA – Probability of Detection
Probability of detecting a failure if it has occurred.
The definition varies for different types of FMEA analysis. Therefore, it is necessary to specify the type of analytical process (for individual failures or for properties).
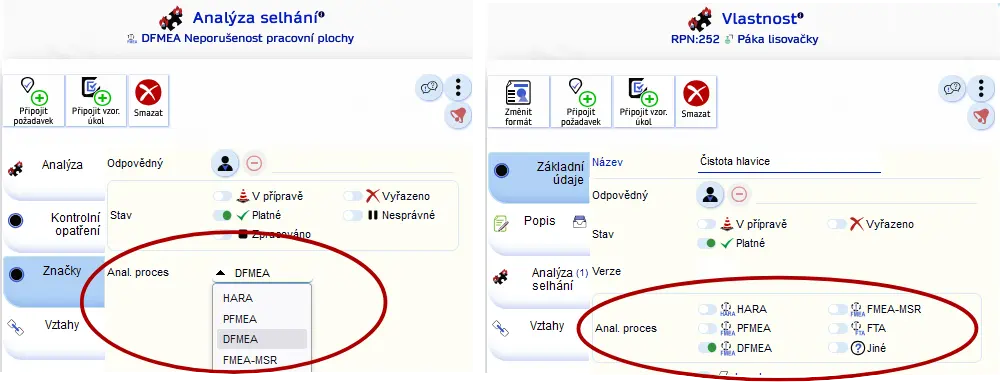
The following overview is based on the automotive industry standard. Before using, check whether it is relevant for your case!
DFMEA
Level 1: It is known that the design cannot fail
Level 2: Verified standard procedures, aging control
Level 3: Verified standard procedures, failure test
Level 4: Verified standard procedures, function pass test
Level 5: Verified standard procedures in the late development phase, aging control
Level 6: Verified standard procedures in the late development phase, failure test
Level 7: Verified standard procedures in the late development phase, low, function pass test
Level 8: New test procedures are used, which are not verified
Level 9: Known tests are not specifically designed to verify potential failures
Level 10: Test procedures have not yet been developed
PFMEA
Level 1: Failure is virtually impossible or cannot go undetected
Level 2: Proven reliable detection methods; machine inspections prevent the occurrence of defective products
Level 3: Proven detection methods; defective products are automatically detected
Level 4: Proven detection methods; reliable inspections detect the problem during production and reject defective products
Level 5: Verified inspections; semi-automatic detection alerts the operator
Level 6: Verified inspections; manual inspection of products or samples detects defects
Level 7: Unverified inspections; semi-automatic detection alerts the operator
Level 8: Unverified inspections depend on manual inspection of products or samples to detect defects
Level 9: It is unlikely that inspections will detect the problem; sample checks may not easily identify the issue
Level 10: It is unlikely or impossible to detect the issue through inspections
FMEA-MSR
Level 1: Always detected – significantly more than 99.9%; the system responds to failures
Level 2: Detected with probability > 99.9%, the system is very likely to identify the failure
Level 3: Automatic detection identifies failures with probability > 99% with a short response time, automatic reaction is highly probable
Level 4: Detection with probability > 97% with medium response variability; the system will usually react to failures
Level 5: Detection with probability 90–97%, with moderate response variability; the system will usually respond automatically to failures
Level 6: The failure is detected by the user or system with probability > 90% and will likely be able to respond
Level 7: Low probability that the us