AyMINE – Technical documentation
Modules
 Task, project & quality management
Task, project & quality management
Manager approval with the task report
Why some data can't be deleted
Adminitration of areas, projects, calendars
Region / project / methodology
Change management process in a project
GDPR and record of qualifications
Qualification of user or contact
Right to Manage Qualifications
Failure Analysis for an Individual Property of a Component or Process
FMEA – Probability of Detection
FMEA – Probability of Occurrence
 Task, project & quality management
Task, project & quality management
Administration of the Task Management Module
System rights for the task management module
Improvements and Preventive Measures
Methodology and Quality Management systems
What a methodology / QMS consists of
Problems, tickets and their management
Collaborative Resolution of Multiple Problems
Customer Service Response Generation
Incident and Quality Issue Management
Objects affected by the problem
Problems, Incidents, Helpdesk Tickets
Return project plan by baseline
Sample tasks and methodologies of the area
Effect of the task on the right to modify the attached object
The person responsible for the task
Working procedure – task definition
Objects related to the task pattern
 Contacts and directories module (CRM)
Contacts and directories module (CRM)
Order overview for customer groups
 Contacts and directories module (CRM)
Contacts and directories module (CRM)
System Permissions and CRM Module Settings
Send bulk messages in compliance with GDPR
How to correctly forget a person's details
Unsubscribe and set preferences
for bulk mail
 Web management and automation
Web management and automation
Receiving a message from the web
Human resources
Personalistics – User Permissions
Human Resources module security
Manage department / division data
Overview of Personnel Information for pracov# Employment Contract
Synchronizing staff and system users
 Products, assets and sales
Products, assets and sales
Received order for goods or services
Finance management
Metrics and Measurements
Technical Modules
Sabre plugin module
Enterprise Architect connector
Database link to Enterprise Architect database
Enterprise Architect connector
System Modules
 The AyMINE Framework Module
The AyMINE Framework Module
AyMINE — Tips for Mobile Usage
Configure how your system looks and works
Gestures and Keyboard Shortcuts
More about how the system works
Private notes and tags for objects
Overview of Modules and Record Types
Filtering in the list of records
 System Management
System Management
Additional functions with files
Copying and moving files between objects
Files (documents) linked to the object
Formatted texts in the application
Gateway settings for external messages
IMP gateway settings for email communication
Internet Call Gateway Settings
Message with the outside world
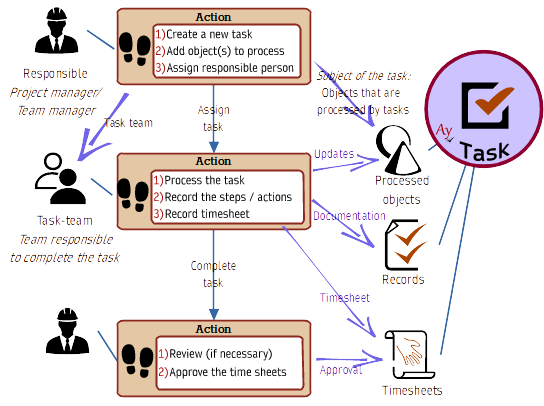
 Timesheet
Timesheet
Activity records are combined with timesheets and by default they are created at the same time. This gives the manager a perfect overview of what work the workers have actually done. The system greatly simplifies work reports while creating accurate records to simplify control.
- A report is linked to both the task and the subject of the task
- Checking Timesheets
- Automate work checks: Use Artificial Intelligence
Timesheets always have to be linked to activity that is reported, which is typically:
The system allows you to link timesheets and activity records to other records, such as an action or a meeting. However, it should always be clear what the worker has been working on. That’s why most reports should be linked directly to the task.
A report is linked to both the task and the subject of the task
Most tasks are linked to one or more objects that are being processed, e.g. all requests from a project that needs to be analyzed are tied to one task.
Most workers work on the basis of a task and even the timesheets are linked to the task: When someone process, for example, 30 calls to customers, he/she reports the work to the task for several hours and does not have to itemize the time to 30 reports of work – single to each called client.
More i topic records linked to the task are in the description of the task.
Checking Timesheets
By linking timesheets directly to the task and processed records, the manager has an overview when approving:
- How many hours the worker declared
- What was the task he was working on
- What was the task subject
- Whether the task is completed
- Who else was involved in the task
Linking reports reveals both fraud and neglect
A fraud is typically shown by an employee or, rather, an external collaborator declaring hours disproportionate to the scope of the task. This is hidden, for example, by declaring hours for a task that was actually being done by someone else. By linking the checks to the task, duplicate reports are immediately clear and alert to the problem.
An overview of hours is displayed in an overview of completed tasks. This makes it possible to quickly identify not only tasks with suspiciously many hours, but also tasks that are short of them.
Managers should carry out these checks not only to avoid paying workers and freelancers for work that was actually not done, but also to check that the work was given the time that they had. This avoids problems in a later audit, which would legitimately reject tasks without actual time worked.
Last, but not least, timesheets linked with tasks are important resource to gather information about the work efficiency that is necessary for planning other project or activity.
What happens to the timesheet when you delete the master record?
Job statements are always tied to the object that the activity was related to – most often a task. If the task was deleted and the report with it, it would break the reporting. Therefore:
- Objects with reported hours cannot be deleted (It is possible to set them as cancelled).
- It is possible to delete entire areas and projects if they are no longer meaningful. In that case, tasks and other objects in them are deleted as well, but all completed job statements are moved to a special area – the storage area. They lose their link to the activity, of course.
Deleting with the Balance Scorecards module active
If the BSC – Balanced Scorecards module is active, statements older than 1 year are not relevant for job statements. The BSC module is replaced by analytical statistics. In this case, the reports are removed together with the main object without replacement.
Automate work checks: Use Artificial Intelligence
The system uses artificial intelligence to detect whether some tasks or some work groups show excessive hours. This makes it possible to detect inefficient work or even fraud in work reports. On the other hand, the system detects tasks that are probably not done properly because they are missing reports.
Artificial Intelligence is also trained to gather data about the time consumed on former projects and adjust plans for a new project. The historical data are essential for proper planning and complete the higher level of the processes quality according to the ISO 33000 standard.
How the artificial intelligence works in a report check
A self-contained algorithm evaluates all tasks and groups them by type and assignment. In the first weeks of use, it collects data and learns about nothing.
After the first stage, it is possible to run an automatic check that automatically alerts managers of anomalies. The manager contributes to learning by approving or rejecting reports. This gives the learning algorithm feedback by which it improves over the long term.
Artificial Intelligence detects even poor quality control by the manager
If the manager of a group does not attend to the check despite the identified anomalies, the artificial intelligence recognizes that the approval system does not lead to a real check. As part of the audit, senior management can point this out
Artificial Intelligence Prevents Bullying
Minor workplace bullying often manifests itself in inadequate tasking of one worker at the expense of the other. The deviations are on both sides – the manager can overload one crew, overload another.
The system also allows for detection of anomalies at the level of job allocation and to point out imbalances. It never decides for itself what is disproportionate and what is right, but the non-standard deviations are brought to the attention of senior management, who decide for themselves whether the anomaly has an obvious justification or needs attention.