AyMINE – Technical documentation
Modules
 Task, project & quality management
Task, project & quality management
Manager approval with the task report
Why some data can't be deleted
Adminitration of areas, projects, calendars
Region / project / methodology
Change management process in a project
GDPR and record of qualifications
Qualification of user or contact
Right to Manage Qualifications
Failure Analysis for an Individual Property of a Component or Process
FMEA – Probability of Detection
FMEA – Probability of Occurrence
 Task, project & quality management
Task, project & quality management
Administration of the Task Management Module
System rights for the task management module
Improvements and Preventive Measures
Methodology and Quality Management systems
What a methodology / QMS consists of
Problems, tickets and their management
Collaborative Resolution of Multiple Problems
Customer Service Response Generation
Incident and Quality Issue Management
Objects affected by the problem
Problems, Incidents, Helpdesk Tickets
Return project plan by baseline
Sample tasks and methodologies of the area
Effect of the task on the right to modify the attached object
The person responsible for the task
Working procedure – task definition
Objects related to the task pattern
 Contacts and directories module (CRM)
Contacts and directories module (CRM)
Order overview for customer groups
 Contacts and directories module (CRM)
Contacts and directories module (CRM)
System Permissions and CRM Module Settings
Send bulk messages in compliance with GDPR
How to correctly forget a person's details
Unsubscribe and set preferences
for bulk mail
 Web management and automation
Web management and automation
Receiving a message from the web
Human resources
Personalistics – User Permissions
Human Resources module security
Manage department / division data
Overview of Personnel Information for pracov# Employment Contract
Synchronizing staff and system users
 Products, assets and sales
Products, assets and sales
Received order for goods or services
Finance management
Metrics and Measurements
Technical Modules
Sabre plugin module
Enterprise Architect connector
Database link to Enterprise Architect database
Enterprise Architect connector
System Modules
 The AyMINE Framework Module
The AyMINE Framework Module
AyMINE — Tips for Mobile Usage
Configure how your system looks and works
Gestures and Keyboard Shortcuts
More about how the system works
Private notes and tags for objects
Overview of Modules and Record Types
Filtering in the list of records
 System Management
System Management
Additional functions with files
Copying and moving files between objects
Files (documents) linked to the object
Formatted texts in the application
Gateway settings for external messages
IMP gateway settings for email communication
Internet Call Gateway Settings
Message with the outside world
 Working procedure – task definition
Working procedure – task definition 
The Working procedure is a specification of the part of a process with all components required for the task execution in the appropriate level of quality.
- A workflow description
- Task patterns
- Task Team
- Multilingual quality system
- How a new task is created from a pattern
Relationships between tasks
- Multiple languages
- More information
FAQ about task patterns / working procedures
Did you get a blank list of sample tasks?
This is not a system error, but there is no sample task available. Either a suitable methodology is not selected for the area or project, or the methodology does not contain any sample tasks for this type of object. You can create a new task for the objects without a pattern link.
The working procedure goes beyond the scope of the regular task description because. Apart of the work steps the description supports definition of a complete sequence of steps and link them to all the running records. It thus fully fulfils the process level of IQMS structured documentation.
A workflow description
The workflow defines part of a task. It is defined by a list of linked subtasks or event deeper hierarchy of tasks. When a real workflow execution is created accoring to the workging procedure, the whole hierarchy of tasks is created, including the dependencies between them.
Examples of compound tasks
Project Stage – Getting Started
Project initiation is a separate stage that includes a number of separate tasks:
- Assessment of project specifics
- Generating a project plan.
- Modifying task assignments – "tailoring".
- Risk analysis
....
All tasks related to the initiation should be part of one task – stage.
Annual internal audit plan
A sample plan is described as a sample task. Individual periodic audits are separate tasks.
Note: The execution of all internal audits follows the same procedure. From an administrative perspective, it would not be efficient to write this procedure separately for all tasks. Therefore, it is possible to attach a methodology to the sample task to be followed. In this case, the methodology should include the workflow of one internal audit.
Name and Description
The name of the task pattern is copied as the name of the task. It should therefore be exactly as the task itself should be named. (Example: Perform a FMEA Security Risk Assessment).
Brief Description (Annotation)
The description will be seen by the staff in the task overview and on the mobile phone. It should therefore be brief but clear at the same time, so as not to confuse what it is based on. (Example: Perform an introductory FMEA to determine the required level of safety SIL of the product).
The length of the brief description is limited to 300 characters.
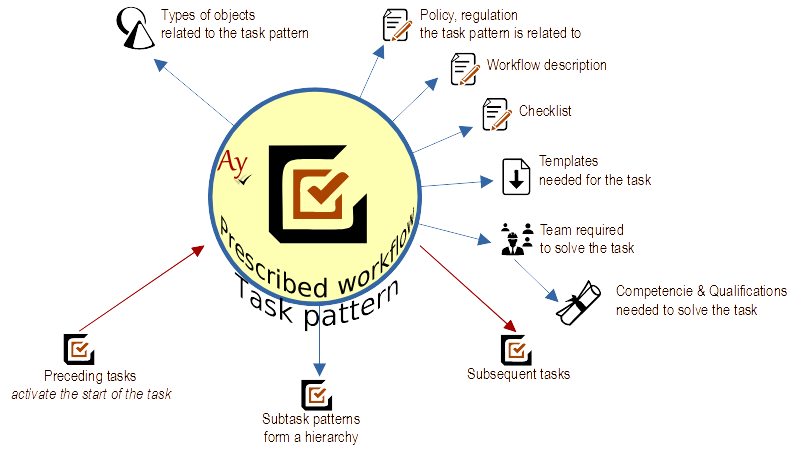
Related Objects
Related objects in the introductory tab describe to which object the task refers.
Correct definition is very important because wrong task definition leads people wrongly. How to correctly determine a related object to a task pattern.
Task patterns
The task pattern defines the task assignment, possibly supplemented by:
a* Procedure instructions on the Steps tab.
- Document templates to be used on between
File
- Another description of why the task is necessary on the
Tasks tab.
Based on the template, the task will be created if someone manually initiates it, or automatically events. To specify automatic triggering, use the Event Binding that triggers on the Events tab.
Workflow steps
The _steps tab should be used to indicate the entire workflow for the team to follow.
If the task pattern is structured into sub-tasks, always indicate the procedure for each sub-task. Never duplicate the description in the main task.
Document templates
- Document templates to be used insert between
File
- Another description of why the task is necessary on the
Tasks tab.
Checklist
The checklist is a description of the steps the task team should take to verify that everything has been done as it should be.
The checklist is copied into the task and the implementing team has the opportunity to fill in the results of the check. It is therefore appropriate to use bullet points directly to confirm that the team has carried out the check. Remember, however, that the bullets should be ticked by someone from the team after each task is completed. It is therefore not advisable to make many of them, because then the worker will be busy ticking instead of checking.
If a sample task has sub-tasks, it is usual for the checklist to have only the last task – for more complex samples it is advisable to put a special verification task at the end. It is useful to combine the verification with, for example, a milestone ending the task
Events
On the Events tab, the business event that starts the task is defined.
Task Team
The workflow defines where everything is involved in solving the task – the task team Within the team you define which team roles are to be involved – e.g. approver, reviewer (verifier). For each team role, you also define the qualifications of the person to be assigned to the role.
If the workflow involves a project task, you assign a role in the task and a project role. When the project plan is generated, the worker from the project team will then be assigned directly to the task team.
More about task teams can be found here.
Sample task relationships
Relationships describe what other components of the methodology (or even other methodologies) are related to the pattern. Relationships are primarily used to manage the sample task.
How to use links between template tasks
Where to use links
- Link a task to other sample tasks that are logically related. For example, if a task processes information generated by another task, it is important to maintain a link between them. When one of them is changed, it is then easy to check the other and assess the effects of the change on the other
- Link to plans that relate to the use of the task
What not to use links for
Don't link to the obligation from which the sample task derives, This link is on the introductory tab (Reasons and Regulations)
Neither should the link to the methodology that the preparer is to follow appear here, as it has its place on the introductory page.
Based on the template, the task will be created if someone manually initiates it or automatically events. To specify automatic triggering, use the Event Binding that triggers on the Events tab.
Multilingual quality system
For multinational teams, but also for deliveries to foreign clients, it is important to have a multilingual methodology. It is not always possible to rely on everyone in the team to read English well enough not to be held back in their work. When you prepare translations for them, you can be sure they know exactly what to do.
Each task pattern and methodology can be saved in any number of languages. Workers will then see the translations in whichever language they choose.
Objects directly support multiple languages, so you don't have to deal with the issue of different versions of the documentation – the sample task is the same, and has the same number. And the user will see both the English original and the Czech translation at the same time. More about the possibility of language versions here.
How a new task is created from a pattern
- The most common way is for a user to create a task within a project or area using the Create Task from Pattern function. Tasks created in this way always belong to the area in which they were created. The user can use patterns from any methodology that is attached to the area.
- A task from a pattern can be created either by people who have the right to the area where the pattern is. They can use the Task button to create a task.
- A task can be created automatically when the event that triggers it occurs. Tasks created in this way are created in the areas and projects where the methodology is attached. One task is created in each active area/project for one trigger event. The task is assigned to people according to the role they are assigned.
- A task can also be created semi-automatically when someone triggers the event that starts the task. To be triggered by an event, the worker does not need to have any rights to the area where the pattern is, nor does he need to know that the pattern exists.
For methods 3 and 4, at least 1 triggering event needs to be associated with the task.
You can read who gets the project task here.
 Relationships between tasks
Relationships between tasks
Pattern tasks can be interconnected by continuities that express the order in which the tasks that are based on them are to proceed. When tasks are created, these dependencies are carried over and are also present between created tasks. Once tasks are created, they are then scheduled so that tasks following another task are scheduled after the previous ones. In order for scheduling to work properly, it is essential that the sample tasks have not only sequences specified, but also the expected duration of the activity.
The relationships between the sample tasks carry over even if the tasks are not created at the same time. If you create a t1 → t2 pattern relationship (the t2 task created from task pattern tp2 is supposed to follow the t1 created from tp1), then you create t1 and sometime later you create t2 so that when you create t2 it will be traced in the t1 area and a link will be created between them.
You can then change the bindings between the created tasks in the project/area independently of the patterns. The templates contain pattern processing, but the project manager or the manager responsible for the area has the possibility to modify the links and the order of the tasks for actual needs.
Multiple languages
If you have a team made up of people of different nationalities, we recommend that you create the methodology in languages that they really understand well. When you prepare translations for them, you can be sure that they will know exactly what to do.
You can save each sample task and methodology in different languages. The staff will then see the translations depending on which language they choose as their own.
More information
The workflow is part of the methodology or documentation of the quality management system. More information about the methodology can be found here.